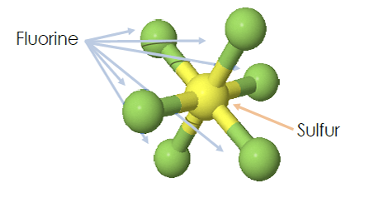
Sulfur hexafluoride, or SF6 gas, is primarily utilized as an electrical insulator and arc suppressant, most commonly by the electrical industry in circuit breakers and switchgear as electrical insulation. SF6 gas is also utilized in a wide array of industries – some of which might even surprise you – such as ophthalmology, windowpanes, and even the shoe industry. SF6 is an artificial gas that is inert, non-toxic and has unmatched dielectric strength as well as great heat-trapping abilities making it such a popularly used gas.
Though SF6 gas is a widely used substance in today’s world, there is a downside to this unique gas. SF6 is known to have a significant global warming potential (GWP) that is 23,500 times larger than that of carbon dioxide, which is why it was named one of the six greenhouse gases that should be controlled within the Global Warming Treaty of 1997. Given that even the smallest of SF6 leaks can greatly harm our environment, it is imperative to avoid any emissions as best we can. Thorough training on gas handling and best practices are a great place to start but ensuring that your facility uses state-of-the-art emission-free SF6 equipment is also essential – from the fittings down to the recovery systems.
Quality Gas Handling Equipment - A Must
Fittings, Valves, and Couplings
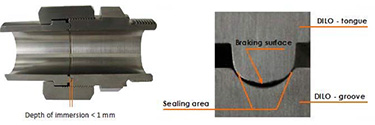
As a first step, it is key to ensure that all fittings used within your equipment are sealed properly and are leak tested. DILO provides state-of-the-art valves and couplings that self-seal and serve as a more dependable substitute for creating a seal with a unique metal-to-metal tongue-and-groove design.
Understanding how different adapter fittings are sealed is an important aspect of proper gas handling. Let’s take a look and identify some of the most commonly used types of fittings and adapters and discuss how to eliminate leakages by using proper assembly and sealing techniques:
Flange Couplings seal two flat surfaces together with the use of an O-ring and a grooved portion on one of the surfaces. When the two sides are assembled with metal-to-metal contact, the O-ring is compressed and creates a seal. These fittings are commonly used on GIE.

Parallel thread fittings are sealed at the “nose ” (bottom of the threaded portion) or at the “face ” (top of the threaded portion below the hex portion) with an O-ring or copper crush gasket. These fittings can easily be reused by replacing the seal and do not require a thread sealant.

NPT (National Pipe Thread) or tapered thread seal when the fitting is tightened and the angled edges of the threads compress against each other due to the taper of the fitting. These are commonly used on adapters, but require a liquid thread sealant /lubricant or Teflon tape to seal properly and are prone to leakage for the following common reasons:
- Not using the correct type of thread sealant
- Incorrect use of thread tape
- The use of galled or damaged NPT thread fittings
- Improper tightening of Connections
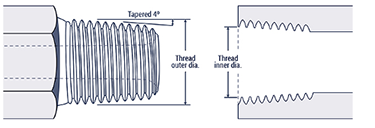
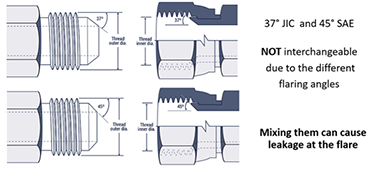
Flare fittings are a type of compression fitting that seals at the tapered portion through direct metal to metal contact or with the use of a copper gasket between the two flared surfaces. Also commonly used and preferred, when compared to NPT, as no additional sealer is needed. Note: Flared type fittings are available in JIC (37 degree) and SAE (45 degree) versions that are NOT interchangeable.
Flared fittings are prone to leakage for the following common reasons:
- Mixing JIC and SAE angels
- Over-tightening
- Indents and Scratches on the flare face
- Forgetting to use a “flare saver” in certain applications
Compression fittings (Swagelok® and Parker® are two common examples) seal by applying a specific amount of torque to a compression nut. When the nut is tightened, the ferrule is compressed between the nut and the receiving fitting. The ends of the ferrule are clamped around the pipe and the middle of the ferrule bows away from the pipe, making the ferrule effectively thicker. The result is that the ferrule seals the space between the pipe, nut, and receiving fitting, thereby forming a tight joint. These fittings require a specific tightening procedure to create a proper seal; over-tightening will damage fitting and cause leaks.
Compression fittings are prone to leakage for the following common reasons:
- Incorrect Installation and tightening
- Ferrules and clamps incorrect positions
- Forgetting to measure the gap

DILO fittings use a tongue and groove design to create a metal-to-metal seal when tightened. DILO fittings remain tight in applications where vibration is present, under positive pressure or vacuum, and regardless of temperature changes and can also be reused indefinitely. They cannot be over tightened, but the sealing surfaces (tongue and groove) must be kept clean.
To learn more about the product range for valves, couplings, adapters, and transition pieces that DILO offers, click here.
Cylinder Heating Blanket
Another piece of SF6 gas handling equipment that is imperative is the cylinder heating blanket. A heater blanket is a device that can be fastened to the bottom portion of a cylinder that helps to prevent the liquefaction of SF6 gas. Cylinders that are filled with SF6 gas typically hold both vapor and liquid forms of the gas. Using cylinder heating blankets allow you to withdraw the greatest amount of SF6 from that cylinder when handling gas, which in turn helps to reduce even more emissions. You can read more about this on our blog post about heater blankets.

Leak Detection Equipment for SF6 Gas
A third apparatus that helps to reduce possible emissions of SF6 gas is leak detection equipment. When it comes to leak detection equipment, the first step is to ensure that you’re using the correct type of equipment for the scope of work. There are a variety of handheld leak detection device options available at DILO which include the SF6 Leak Pointer/Sniffer, the SF6 Gas Leak Detector, and the Portable SF6 Gas Monitor & Leak Detector.
The3-033-R002 – leak detector will detect all Halogenated (Containing Chlorine or Fluorine) refrigerants. They are an inexpensive tool to keep in a toolbox or work vehicle and are widely used by field-level personnel.
The 3-033-R502- Is ideal if you need something to detect smaller leaks with no cross-sensitivity to other gasses. This device is equipped with an advanced NDIR (non-dispersive infrared) sensor specifically calibrated to detect SF6 gas. The unit detects how much SF6 is present by the amount of light that doesn’t make it through the sensor due to it being absorbed by SF6 – to put it very simply.
It can also be used to complement PPE when entering vaults or other areas where gas can accumulate since it can quantify the level of SF6 in PPMv. The OSHA threshold level for SF6 in the work environment is 1,000 PPMv.

Another option in terms of leak detection equipment is the SF6 Gas Room Monitor, which provides continuous monitoring for leaks in as many as 16 individual zones. It is important to consider a room monitor system for indoor Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) applications because SF6 will displace oxygen, creating a potential for asphyxiation in indoor environments. With this device, there is also no calibration required and the low detection limits allow for the quick discovery of any SF6 gas accumulations that might occur within a facility.

Tracking Gas Volume
Devices that have the ability to track gas volume are also an important component in the prevention of SF6 gas leaks. DILO’s Mass Flow Meter allows you to accurately account for gas movements to and from the circuit breaker.

The SF6 Cylinder Scale is another device that is able to determine gas volume within cylinders. This electronic weight scale quickly and easily determines the quantity of gas when filling a gas bottle.
Do you have any cylinders that have been stored for a while? In the following Pro-tip video, Tobias Probst goes over another useful tip when it comes to testing SF6 cylinders that have been sitting in storage for some time.
Testing and Gas Analysis
The use of a measuring device that has an internal recovery feature or is compatible with a recovery bag is also important in order to avoid venting SF6 into the atmosphere during testing. The recovery bag is an easy economical method for gathering gas in the event that it cannot be directly pumped back into the circuit breaker.

Another key device to safely test and analyze gas is a zero emissions analyzer. An analyzer like this can internally store the measured gas within the device, in an external gas cylinder, or within an external gas collecting bag and gas is not vented to the atmosphere upon completion of a measurement.

Recovery Systems
Lastly, another important factor to reduce potential SF6 gas emissions is to ensure that you are using not only the correct size but also the right type of recovery unit for the quantity of SF6 gas that you’re working with. DILO offers an SF6 Time Calculation App that can help you determine which gas cart is suitable for your purpose. Also, be sure to check out our blog post on selecting the correct SF6 gas recovery system!

Training
As you can see, there is a lot of SF6 gas handling equipment involved in zero-emission gas handling. One of the most important and effective ways to prevent SF6 emissions is the proper training of the personnel who are handling the gas. Even with having all the latest state-of-the-art equipment, an unqualified/untrained technician can unknowingly create SF6 emissions.
Are you looking for training opportunities for you or your staff? The SF6 Gas Management Seminar in November is a cost-effective and great way to learn more from industry experts and learn by doing in our hands-on break-out sessions.
As always, please contact us with any questions you might have about gas handling or equipment. DILO is passionate about preventing SF6 emissions and our team of SF6 experts is always happy to help!