Understanding Gas Purity
Gas purity refers to the concentration of the desired gas component with a single gas or within a gas mixture. In the context of electrical applications, even minor impurities can significantly impact equipment performance and safety. Here's a breakdown of the significance of gas purity for different gases:
- SF6 (Sulfur Hexafluoride): Widely used for insulation due to its excellent dielectric properties. Impurities can decrease its insulating strength, leading to arcing and equipment failure.
- C4 (fluoronitrile mixtures) / CA (dry-air mixtures) : Emerging alternatives to SF6 with lower environmental impact. Maintaining purity and gas mixture ratios ensures optimal insulation and current interruption capabilities.
- Hydrogen: Used in some applications for cooling and switching. Impurities, particularly moisture, can affect its electrical conductivity and lead to corrosion.
- Noble Gases (e.g., Helium, Xenon, Argon, Neon): Employed for inert atmospheres and pressure applications. Maintaining purity minimizes contamination and ensures proper system function.
Impure gases can also pose health risks. SF6 impurities, such as SO2, are acid vapors that pose a risk to human health if inhaled or ingested. Therefore, it is essential to know the purity of any gas prior to handling. (Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on SF6 Emissions).
The Framework for Gas Purity Regulations
International and national regulatory bodies establish guidelines for acceptable gas purity levels. These standards ensure the safe and environmentally responsible operation of electrical equipment. Here are some key players:
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): This body sets international standards for electrical equipment, including specifications for SF6 gas purity (DILO Certified SF6 Gas).
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Regulates SF6 emissions in the United States (SF6 Emission Reduction Partnership).
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC): This commission oversees interstate electricity transmission and mandates reporting of SF6 leaks and emissions (FERC Order on Reliability Standards for Inverter-Based Resources).
Regular gas purity checks ensure compliance with these regulations.
Methods for Testing Gas Purity
The choice of testing method depends on the specific gas and the desired level of detail. Here's an overview of standard techniques:
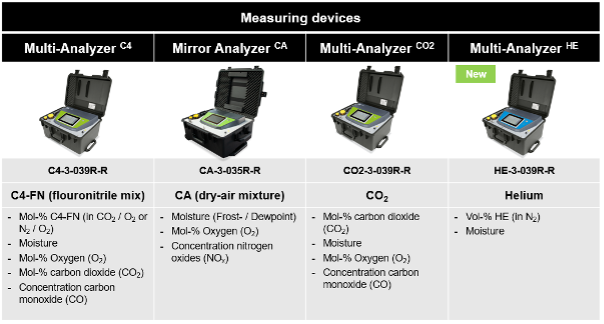
- SF6 Gas Analyzers: Portable and user-friendly, these analyzers provide quick and accurate on-site measurements of SF6 purity and common contaminants using Velocity of Sound (Learn More About SF6 Gas Analyzers: click here)
- Velocity of Sound a practical method for SF6 purity measurement. In each substance the sound has a different speed. For example, in pure Air = 330 m/s and pure SF6 =129m/s. The achievable accuracy is generally: +/- 0.5% by volume.

- C4 Gas Mixture Analyzers: while similar to portable SF6 analyzers, C4 gas analyzers utilize Non-Dispersive Infrared Measurement (ND-IR).
- ND-IR Sensors measure the signal strength of a specific molecular oscillation stimulated by the absorption of a photonic wavelength specific to the molecule. By choosing the corresponding oscillation, the sensors target molecules selectively. As a consequence, other gases do not affect the measurement result. The achievable accuracy is generally: +/- 0.1% by volume.
- Gas Chromatography (GC): This laboratory technique offers a more in-depth analysis, identifying and quantifying a wider range of impurities present in the gas mixture.
Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Gas Purity
Maintaining the purity of gases used in various industrial applications is crucial for safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Here's a general guide to the process, though the specific steps may vary depending on the type of gas and the desired level of detail.
Preparation
- Safety First: Always consult the relevant safety data sheets (SDS) for the gas you're working with and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, safety glasses, and respirators if necessary.
Gather Equipment: The equipment needed will depend on the chosen testing method. Common tools include: - Portable Gas Analyzers: These handheld devices provide quick on-site measurements of gas purity and common contaminants for various gases using techniques like infrared spectroscopy.
- Gas Sampling Kit: For laboratory analysis using gas chromatography (GC), a proper sampling kit is required to collect a representative gas sample without introducing contamination.
- Leak Detection Equipment: Maintaining system integrity is vital. Utilize leak detection equipment or chambers specifically designed for the gas you're testing to identify potential leaks and minimize gas loss.
Testing Procedure
- SF6: Utilize an SF6 gas analyzer to directly measure SF6 concentration (purity) and common contaminants like moisture and decomposition products on-site. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper sample collection and analysis.
- C4 (fluoronitrile mixtures) / CA (dry-air mixtures): Similar to SF6, portable analyzers are available for field testing of C4 and CA gas mixtures. GC analysis may be required for a more comprehensive evaluation, especially when investigating unidentified impurities.
- Noble Gases: These gases are typically inert and have high purity levels. Helium for example, can be measured with a field levelHe-gas analyzer. GC analysis can be used for detailed compositional analysis if needed, particularly when verifying the exact gas mixture or identifying unexpected contaminants.
Interpreting Results
Compare the test results to the established standards for the specific gas and application. Resources like the IEC 60856-2:2020 - Sulphur hexafluoride for electrical equipment - Specifications: see here (from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)) provide detailed guidance on acceptable purity levels. If the results indicate excessive impurities, further investigation may be necessary to determine the source of contamination. Depending on the severity, gas treatment or replacement might be required to ensure continued safe and efficient operation.
Maintaining Gas Purity
Best practices for handling, storing, and using critical gases are essential for maintaining purity:
Use Certified Gas Suppliers: Ensure your gas supplier provides high-quality, certified gas to minimize initial contamination.
Proper Gas Handling Equipment: Utilize dedicated equipment for each gas type to prevent cross-contamination.
Leak-Tight Systems: Regularly inspect equipment for leaks and ensure proper sealing of gas compartments. Early detection and repair of leaks are crucial for minimizing gas loss and maintaining purity.
Regular Testing: Conduct routine gas purity checks as recommended by the equipment manufacturer and regulatory guidelines. Early detection of rising impurity levels allows for timely intervention and helps prevent equipment failure and environmental emissions.
Proper Gas Storage: Store gas cylinders in cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Follow proper handling procedures to minimize accidental releases and maintain gas integrity.
Training: Personnel handling and maintaining gas-insulated equipment should receive proper training on gas safety procedures, including leak detection, purity testing protocols, and emergency response procedures.
Examples of Why Gas Purity Inspections are Important
Scenario 1: Reduced Insulation Strength due to Impure SF6
A utility company experiences unexpected equipment failure in a gas-insulated substation. Investigation reveals high moisture levels in the SF6 gas, exceeding the recommended purity standards outlined in the IEC 60856-2:2020 - Sulphur hexafluoride for electrical equipment - Specifications: see here (from the International Electrotechnical Commission). This moisture contamination compromised the insulating properties of the SF6, leading to arcing and equipment damage. The incident highlights the importance of regular gas purity checks using SF6 gas analyzers or other appropriate methods to prevent costly outages and safety hazards.
Scenario 2: Environmental Benefits of Maintaining C4/CA Purity
An electricity transmission company implements a program for regular purity checks of their C4/CA gas-insulated equipment. By ensuring minimal leakage and maintaining gas purity through proper handling practices and filtration processes, the company significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional SF6 systems. This demonstrates the environmental benefits of using SF6 alternatives and maintaining their purity for responsible operation.
Related Article: How Does the SF6 Filtration and Purification Process Work?
Regulations and Reporting Requirements
Maintaining gas purity is crucial not only for safety and equipment performance but also for aligning with environmental regulations. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates SF6 emissions under the Significant New Alternative Policy (SNAP) program . Additionally, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) mandates electric utilities to report SF6 leaks and emissions exceeding specific thresholds . Regularly monitoring gas purity helps companies stay compliant with these regulations and avoid potential penalties.
Conclusion
Maintaining the purity of critical gases is paramount for ensuring safe, efficient, and environmentally conscious operation. By understanding the importance of gas purity, adhering to regulatory standards, and implementing best practices for testing and maintenance, utilities and electrical equipment operators can minimize risks, optimize performance, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Do you have any questions on gas purity? We are here to help!
Contact Us