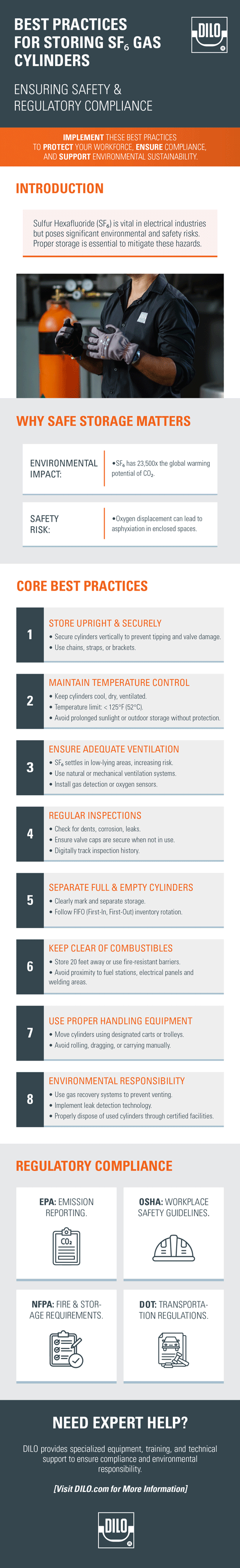
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) is a widely used gas in the electrical industry, and proper SF₆ gas cylinder storage is essential to prevent emissions and ensure compliance with safety standards. It plays a critical role in high-voltage switchgear, circuit breakers, and other equipment due to its arc-quenching and insulating capabilities.
However, SF₆ also presents significant environmental risks. With a global warming potential roughly 23,500 times greater than CO₂ over 100 years and an atmospheric lifetime of 3,200 years, any unintentional release is a serious concern. For this reason, proper storage and handling are environmental and regulatory imperatives.
While SF₆ is non-toxic, non-flammable, and chemically stable, it can displace oxygen in enclosed spaces, creating a risk of asphyxiation. This property, combined with its high global warming potential, makes strict control and safe storage practices absolutely essential.
Storing Cylinders Upright and Securely
When storing SF₆ gas cylinders, always keep them in an upright position. This minimizes internal pressure fluctuation and protects the valve from damage. Since the valve is the most delicate part of the cylinder, securing the cylinder in place with chains, straps, or mounting brackets helps prevent tipping and accidental impact.
Each cylinder should be individually restrained to avoid domino effects, especially in facilities that store multiple units. For a detailed guide on the do's and don'ts of SF₆ gas handling, refer to this comprehensive presentation on the subjectdo's and don'ts of SF6 gas handling.
Maintaining Temperature Control
Temperature regulation is another critical aspect of SF₆ storage. Cylinders should be kept in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated space. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures or direct sunlight can lead to increased internal pressure and, in extreme cases, rupture. The storage temperature should not exceed 125°F (52°C).
Outdoor storage, while not ideal, must be carefully managed with protective covers and shade structures to keep cylinders within safe temperature limits. Temperature regulation is a cornerstone of safe SF₆ gas storage, as it helps reduce the risk of high-pressure incidents.
Ensuring Ventilation in Storage Areas
Although SF₆ is inert, its tendency to displace air makes ventilation a top priority. Being heavier than air, SF₆ settles in low-lying areas, which can lead to oxygen displacement and pose a serious risk in confined spaces. All storage areas must be adequately ventilated, either naturally or through mechanical systems, to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases. In areas where leaks could pose a significant risk, installing oxygen sensors or gas detection systems adds an essential layer of protection.
Conducting Regular Cylinder Inspections
Routine inspection of SF₆ cylinders is essential for safety and compliance. Inspect for physical damage, such as dents, corrosion, or rust, particularly around the base and valve. Leaks can sometimes be detected through sound, frost buildup, or byproducts of chemical reactions.
When not in use, cylinders should have their protective valve caps securely in place. Any compromised cylinders must be clearly marked and removed from service for evaluation. Digitally tracking inspection history can streamline compliance and enhance maintenance routines.
For more detailed tips on handling SF6 gas, check out ourSF6 gas handling tips.
Separating Full and Empty Cylinders
Organizing your storage area to keep full and empty cylinders separate helps avoid confusion, promotes efficient use, and supports proper inventory rotation. This also makes it easier to identify which cylinders require replacement or return to the supplier.
A first-in, first-out (FIFO) usage method is recommended to prevent prolonged storage of any single cylinder, which may lead to seal or valve degradation over time. Labeling systems, color-coded caps, or designated shelves can help maintain this organization.
Keeping Cylinders Clear of Combustibles
Though SF₆ itself is non-flammable, storing it near combustible materials is a safety hazard and violates fire code regulations. Cylinders should be placed at least 20 feet away from flammable substances or separated by a noncombustible wall at least five feet high with a 30-minute fire resistance rating.
Avoid placing SF₆ storage near fuel stations, paint supplies, electrical panels, or welding equipment. This precaution is especially important in industrial facilities with diverse operations occurring nearby.
Using Proper Handling Equipment
Moving gas cylinders should never be done by rolling or dragging. Instead, use carts or trolleys specifically designed for high-pressure gas containers. These carts typically feature secure straps or clamps to hold the cylinder upright and prevent tipping during transport.
Ensure that all staff are trained in cylinder handling procedures and are aware of the hazards associated with improper transportation. Always leave the valve cap on during transport and inspect the route to ensure it is free of steps, slopes, or other obstacles that could lead to accidents.
Environmental Responsibility and Emissions Control
Given SF₆’s severe environmental impact, preventing emissions must be a central part of any storage or handling policy. This includes the use of gas recovery systems during equipment maintenance or decommissioning, rather than venting gas to the atmosphere.
Facilities should consider implementing leak detection technologies such as infrared cameras or ultrasonic detectors to identify leaks early. Personnel handling SF₆ should be trained and certified in proper handling methods and emission prevention practices.
Used or expired cylinders must be returned to the supplier or sent to a certified disposal facility and never discarded with general waste. Ensure you're following the correctSF6 safe handling procedures to prevent potential leaks and environmental hazards.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Multiple regulatory bodies govern the storage and handling of SF₆. The EPA monitors emissions and may require reporting from specific users, while OSHA regulations address workplace exposure and safety procedures.
Fire codes issued by the NFPA establish separation and containment requirements, while DOT regulations cover transportation and labeling of cylinders. Staying current with these regulations is crucial to avoid fines, ensure safety, and demonstrate environmental stewardship.
Regulatory audits often include verification of storage conditions, inspection logs, and tracking of cylinder usage, so proper documentation and transparent procedures are essential.
To learn more about proper SF6 gas handling, visit ourSF6 handling page.
The Bottom Line
Proper storage and handling of SF₆ cylinders are fundamental to ensuring worker safety and reducing environmental harm. When storing cylinders upright and secured, maintaining appropriate temperatures, providing adequate ventilation, performing regular inspections, keeping inventory organized, adhering to safe handling practices, and addressing environmental responsibilities, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with SF₆ use.
These best practices not only protect your personnel and assets but also align your operations with both industry standards and environmental commitments. To strengthen your approach to SF₆ gas management, consider working with providers who specialize in this area.
At DILO, we offer equipment, training, and technical support for leak detection, gas recovery, and safe storage infrastructure, helping you meet sustainability and compliance goals.
For more information and tailored solutions, contact us. We are happy to help!