Xenon Gas History
Xenon gas was discovered in 1898 by Morris Travers and William Ramsay. This pair of chemists previously made various chemical properties of xenon breakthroughs with similar materials by extracting neon, krypton, and argon from liquid air, which played a key role in their ability to successfully identify xenon through their work at the University College London.
The discovery of xenon was a natural progression from their previous work with krypton, as it involved refining techniques that enabled the isolation of xenon from the broader mixture, highlighting its distinct properties as a noble gas. Its unique blue glow was an early indicator of potential uses for the new gas, and Ramsay and Travers named it after the Greek term Xenos.
This information was later used to identify uses for xenon in the medical area. Understanding the xenon element's discovery and history is crucial for appreciating its modern applications.
Xenon Gas Properties and Uses
Xenon is a scarce trace gas found only naturally at approximately one part per 20 million in the Earth's atmosphere. However, its unique properties make it a highly desirable gas for a wide range of xenon uses, which means that significantly more of this gas is commercially made than what can be found and gathered.
This type of xenon gas is a byproduct of fractional distillation, which involves splitting air into nitrogen and oxygen. Xenon is then further isolated from the mixture of krypton and xenon produced by the initial liquid oxygen. How krypton is removed from xenon gas involves additional distillation steps to separate the two gases based on their different boiling points.
Xenonhas also shown promise in the medical area, particularly in anesthesia and imaging, due to its non-reactive nature and ability to produce clear images in diagnostic equipment.
For those wondering what xenon is, it is essential to note that its properties extend beyond its rarity, making it valuable in various applications, from lighting to medical imaging. The xenon definition encompasses its status as a noble gas, characterized by its inertness and distinct blue glow when electrified.
Xenon Gas Safety Concerns
While xenon gas can have a wide range of beneficial uses, this gas is also capable of presenting significant safety hazards if it is not used properly.
Xenon gas is mainly known for causing asphyxiation if too much is inhaled, but there are also several other potential concerns that can be associated with this gas if it is handled or stored carelessly.
Many of these potential problems only arise when xenon gas is not handled safely, which means there is generally no reason to avoid using it as long as proper precautions are taken to ensure it is used in a safe environment.
Here are some of the most significant safety concerns linked to xenon gas to be aware of:
Asphyxiation and Other Inhalation Symptoms
Xenon gas is a type of simple asphyxiate, meaning inhaling too much can prevent your body from receiving enough oxygen. Severely limited oxygen levels can lead to loss of consciousness and even death, while smaller amounts of xenon gas inhalation may cause varying levels of nausea, dizziness, and vomiting.
Not being able to access an adequate amount of oxygen can lead to significant confusion, which can cause accidents and injuries that result from being unable to make reasonable decisions.
Lost consciousness also makes it impossible to move to a safer area or make other simple changes to improve an unsafe situation. It is crucial to avoid being alone when working with xenon gas.
Early asphyxiation is characterized by the rapid and largely unsuccessful respirations associated with attempting to breathe properly and not being able to obtain enough oxygen.
This quickly progresses to diminishing mental alertness and muscular coordination as systems begin to be impacted and eventually shut down due to a lack of oxygen. Later symptoms include convulsions and total loss of consciousness, which can quickly lead to death if the individual is not quickly moved to a safer area that has not been infiltrated with xenon gas to receive medical attention.
Improper Storage Concerns
The unique characteristics of xenon gas mean that it must be stored properly to avoid inadvertently creating a hazardous situation. This gas dissolves if it is stored in most types of plastic or rubber containers, eventually allowing it to escape from its container and be unable to be used.
Xenon gas can generally be safely stored in most types of metal or glass containers as long as they are properly sealed and kept at an ideal temperature and pressure level.
However, it is still important to carefully monitor containers of stored xenon gas regularly to ensure that levels remain where they are intended to be because even seemingly minor leaks can lead to significant safety concerns once a considerable amount of xenon gas is released into the air in the area in which the xenon gas is stored.
This is particularly true because xenon is an odorless gas, meaning that issues will likely go unnoticed until they cause significant illness.
Disposal Concerns
While xenon gas is not necessarily considered to be one of the most dangerous substances to dispose of, it does have the potential to negatively impact nearby air, water, and other aspects of the environment if it is not disposed of properly.
This means that it is important to be aware of and adhere to local, state, and federal regulations when disposing of unneeded xenon gas to ensure that it is done so as safely as possible.
Safely disposing of xenon gas generally consists of venting gas in an outdoor area as far from people and buildings as possible. Rather than disposing of compressed gas cylinders yourself, you should typically return these materials to the supplier you purchased them from so that that company can ensure that they are disposed of properly.
Ensure the cylinder valve is tightly sealed before shipping these containers back to the manufacturer to prevent any residual xenon gas that is still present from escaping into the environment.
Xenon Gas Common Uses
Xenon gas's unique characteristics make it a practical choice for creating various types of specialized lights, and it can also play a key role in supporting the operations of other scientific fields. Here are some of the most common uses of xenon gas!
Lights
The unique properties of xenon gas allow it to play a vital role in creating exceptionally bright lights. It is best known for making many of the brightest headlights possible, all characterized by their distinct blue or lavender glow. Other common uses of xenon-based light include camera flashbulbs, tanning beds, and lamps that are used for food preparation and processing.
Medicine
Xenon gas can also play an essential role in the medical field because it can be used to create certain types of medications and xenon in MRIs and other tests that utilize specialized lights.
Space Exploration
This gas is also used to keep various satellites in orbit and contributes to the functionality of particular spacecrafts. Because inert xenon does not cause corrosion, it is ideal for use in space environments. Xenon ion propulsion systems are designed to keep the satellite on station. The xenon fuel weighs only one-tenth as much as an equivalent amount of chemical fuel, allowing satellites to carry enough xenon to remain on station for up to 15 years.
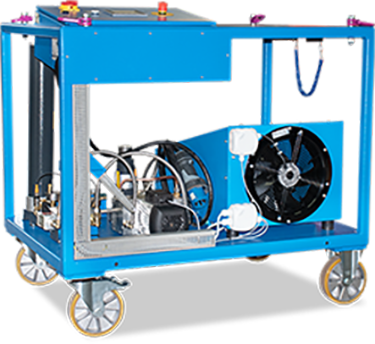
DILO's System for Xenon Gas Recovery and Filtering
At DILO, we prioritize xenon gas handling equipment safely throughout every stage of the recovery and filtering process to ensure it can be used as effectively as possible without presenting unnecessary safety hazards.
Our equipment is key in filling and recovering xenon and other noble gases, ensuring emission-free designs so these gases are managed safely and professionally.
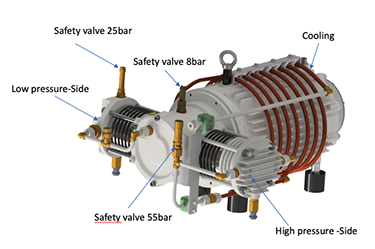
Compressors ‘Made by DILO’
Special gasses require special gas handling systems. The B280R51, 2-stage piston compressor, manufactured by DILO, for non-explosive industrial gasses, is the ideal high-performance compressor system for your special applications.
The emission-free and entirely oil-free compressor features a compact design. The compressor is air-cooled, thus, complicated water cooling is not necessary.
Advantages:
• Entirely oil-free compressor
• Gas-tight version (no gas loss into the atmosphere)
At DILO, we prioritize safety, reliability, and overall economic efficiency, with each equipment design. Contact us today to learn more about our xenon gas recovery and filtering services.